( I ignore the part of the model to simplify my example code )
... run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE) run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata() ... with tf.Session(config=config) as sess: init.run() for epoch in range(n_epochs): for iteration in range(10): sess.run(training_op, feed_dict={X: picture, y:picture_label}, options=run_options, run_metadata=run_metadata) fetched_timeline = timeline.Timeline(run_metadata.step_stats) chrome_trace = fetched_timeline.generate_chrome_trace_format() with open('timeline_step_%d.json' % iteration, 'w') as f: f.write(chrome_trace)
.
|-- timeline_step_1.json
|-- timeline_step_2.json
|-- timeline_step_3.json
|-- timeline_step_4.json
...
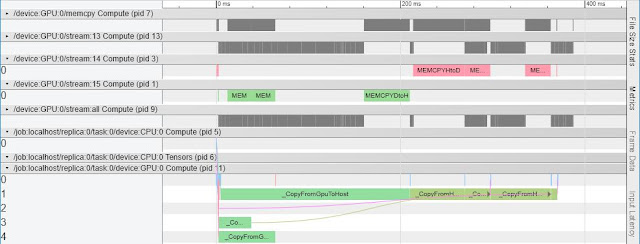
Once you get these files, you can use Chrome's app ==> chrome://tracing/
Load your timeline json file and then see the profiling chart in Chrome as follows:
For more information, you can check this page.
What if you want to know what the GPU peak memory usage? In TensorFlow's contrib module, there is an op named: memory_stats_ops, which provides some GPU memory used information.
from tensorflow.contrib.memory_stats.python.ops import memory_stats_ops
...
max_bytes_in_use = sess.run(memory_stats_ops.MaxBytesInUse())/1e6
Result==>
step:0, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:1, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:2, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:3, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:4, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:5, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:6, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
step:7, Max Memory used: 78.05 MB
...
If you really eager to dig more information in timeline function we introduced above, you probably can use the following code to dump all the data in step_stats:
for device in run_metadata.step_stats.dev_stats:
device_name = device.device
print("[DEBUG]...device:", device.device)
for node in device.node_stats:
print("[DEBUG].......node_stats:", str(node))
Result==>
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "fc1/fc1/MatMul:MatMul"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599000\nop_end_rel_micros: 3\nall_end_rel_micros: 3\n')
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "fc1/fc1/MatMul:MatMul"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599022\nop_end_rel_micros: 105\nall_end_rel_micros: 105\n')
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "train/gradients/zeros_1:Fill"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599130\nop_end_rel_micros: 5\nall_end_rel_micros: 5\n')
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "fc1/fc1/BiasAdd:BiasAdd"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599137\nop_end_rel_micros: 3\nall_end_rel_micros: 3\n')
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "fc1/fc1/Relu:Relu"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599164\nop_end_rel_micros: 2\nall_end_rel_micros: 2\n')
('[DEBUG]......node_stats:', 'node_name: "output/output/MatMul:MatMul"\nall_start_micros: 1535533978599209\nop_end_rel_micros: 9\nall_end_rel_micros: 9\n')
...
Or you are curious about the parameters/weights in TensorFlow's trainable variables, you can do this way to dump data in variables:
# Get all trainable variables
v = tf.trainable_variables(scope=None)
...
weights = sess.run(v[0])
print("variable:%s, data:%s "%(v[0].name, weights))
# If you know the variable's name,
# you also can do this way to pick up the variable:
# Desired variable is called "conv1/kernel:0".
# my_var = [v for v in tf.trainable_variables() if v.name == "conv1/kernel:0"][0]
# ==> <tf.Variable 'conv1/kernel:0' shape=(3, 3, 1, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
Result==>
variable:conv1/kernel:0, data:[[[[ 8.93475637e-02 -3.23383175e-02 1.23850964e-01 1.37569442e-01
1.14479534e-01 1.29268140e-01 7.13080689e-02 1.24710046e-01
1.82287507e-02 -7.33613148e-02 -3.20041701e-02 1.38989389e-01
-1.05456695e-01 1.42283797e-01 3.79515365e-02 5.41552491e-02
7.43211359e-02 1.03672653e-01 4.35486808e-02 1.28800021e-02
1.11616381e-01 -7.48727769e-02 7.90673792e-02 7.89501593e-02
-1.17458910e-01 8.51897225e-02 8.71774256e-02 -1.80314970e-03
1.06145740e-01 1.09351836e-01 -8.27629194e-02 -9.13871154e-02]]
...
All these pieces of code could be difficult for you to verify. So, the following code is a complete example ( for GPU). Here you go:
import numpy as np
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib.memory_stats.python.ops import memory_stats_ops
from tensorflow.python.client import timeline
batch_size = 32
n_epochs = 1
height = 28
width = 28
channels = 1
n_inputs = height * width
conv1_fmaps = 32
conv1_ksize = 3
conv1_stride = 1
conv1_pad = "SAME"
conv2_fmaps = 64
conv2_ksize = 3
conv2_stride = 1
conv2_pad = "SAME"
conv2_dropout_rate = 0.25
pool3_fmaps = conv2_fmaps
n_fc1 = 128
fc1_dropout_rate = 0.5
n_outputs = 10
with tf.name_scope("inputs"):
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, n_inputs], name="X")
X_reshaped = tf.reshape(X, shape=[-1, height, width, channels])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size], name="y")
training = tf.placeholder_with_default(False, shape=[], name='training')
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(X_reshaped, filters=conv1_fmaps, kernel_size=conv1_ksize,
strides=conv1_stride, padding=conv1_pad,
activation=tf.nn.relu, name="conv1")
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(conv1, filters=conv2_fmaps, kernel_size=conv2_ksize,
strides=conv2_stride, padding=conv2_pad,
activation=tf.nn.relu, name="conv2")
with tf.name_scope("pool3"):
pool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="VALID")
pool3_flat = tf.reshape(pool3, shape=[-1, pool3_fmaps * 14 * 14])
pool3_flat_drop = tf.layers.dropout(pool3_flat, conv2_dropout_rate, training=training)
with tf.name_scope("fc1"):
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(pool3_flat_drop, n_fc1, activation=tf.nn.relu, name="fc1")
fc1_drop = tf.layers.dropout(fc1, fc1_dropout_rate, training=training)
with tf.name_scope("output"):
logits = tf.layers.dense(fc1, n_outputs, name="output")
Y_proba = tf.nn.softmax(logits, name="Y_proba")
with tf.name_scope("train"):
xentropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(xentropy)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer()
training_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)
with tf.name_scope("eval"):
correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, y, 1)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, tf.float32))
with tf.name_scope("init_and_save"):
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/MNIST_data/data/")
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("./event_graph")
writer.add_graph(graph=graph)
v = tf.trainable_variables(scope=None)
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True)) as sess:
init.run()
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for iteration in range(mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size):
X_batch, y_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(training_op, feed_dict={X: X_batch, y: y_batch}, options=run_options, run_metadata=run_metadata)
max_bytes_in_use = sess.run(memory_stats_ops.MaxBytesInUse())/1e6
print("step:%i, Max Memory used: %.2f MB "%(iteration, max_bytes_in_use))
weights = sess.run(v[0])
print("variable:%s, data:%s "%(v[0].name, weights))
for device in run_metadata.step_stats.dev_stats:
device_name = device.device
print("[DEBUG]...device:", device.device)
for node in device.node_stats:
print("[DEBUG]......node_stats:", str(node))
fetched_timeline = timeline.Timeline(run_metadata.step_stats)
chrome_trace = fetched_timeline.generate_chrome_trace_format()
with open('timeline_step_%d.json' % iteration, 'w') as f:
f.write(chrome_trace)
P.S: For the explanation of GPU stream and CPU task in chrome://tracing, please check it out:
https://qiita.com/jack_ama/items/c74aeecc78a77e6c9097
No comments:
Post a Comment